HAProxy basic configuration on Ubuntu 14.04
HAProxy is a free, very fast and reliable solution offering high availability, load balancing, and proxying for TCP and HTTP-based applications. It is particularly suited for very high traffic web sites. Over the years it has become the de-facto standard opensource software load balancer, is now shipped with most mainstream Linux distributions, and is often deployed by default in cloud platforms.
This post describes the steps used to install and deploy a basic configuration of HAProxy on Ubuntu 14.04.
The architecture is composed by three ubuntu virtual machine:
- Hostname: node1 IP Address: 172.17.0.101
Description: Server used to install and to run haproxy - Hostname: node2 IP Address: 172.17.0.102
Description: Server running already apache on port 80 - Hostname: node3 IP Address: 172.17.0.103
Description: Server running already apache on port 80
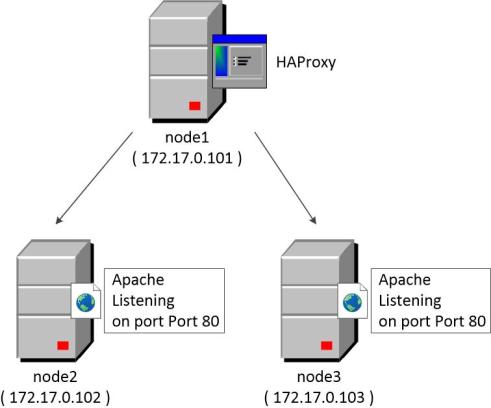
The haproxy software on server node1 will be used to balance the apache service installed on node1 and node2.
- Install haproxy software
root@node1:~# apt-get install haproxy
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
Suggested packages:
vim-haproxy
The following NEW packages will be installed:
haproxy
0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 74 not upgraded.
Need to get 453 kB of archives.
After this operation, 822 kB of additional disk space will be used.
Get:1 http://it.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ trusty/main haproxy amd64 1.4.24-2 [453 kB]
Fetched 453 kB in 0s (568 kB/s)
Selecting previously unselected package haproxy.
(Reading database ... 68156 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack .../haproxy_1.4.24-2_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking haproxy (1.4.24-2) ...
Processing triggers for ureadahead (0.100.0-16) ...
ureadahead will be reprofiled on next reboot
Processing triggers for man-db (2.6.7.1-1ubuntu1) ...
Setting up haproxy (1.4.24-2) ...
Processing triggers for ureadahead (0.100.0-16) ...- Enable haproxy init.d script
For default haproxy has been disabled. Enable HAProxy editing /etc/default/haproxy and setting ENABLED variable to 1
root@node1:~# sed -i "s/ENABLED=0/ENABLED=1/g" /etc/default/haproxy- Add the first frontend and backend in haproxy configuration
Edit the haproxy configuration file ( /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg ) and add the first frontend and backend sections.
These two sections showed below allow to balance each request coming to 172.17.0.101 port 80 to the ports 80 of the two web servers node2 and node3 (ip addresses 172.17.0.101 172.17.0.102).
The option “check” in the last two lines is used to verify using a tcp connection that each web server is available. If one of backend server is offline or doesn’t respond to tcp connection on port 80, haproxy redirects all the requests on the other webserver.
The balancing method used by default in haproxy is round robin.
root@node1:~# cat /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
global
log /dev/log local0
log /dev/log local1 notice
chroot /var/lib/haproxy
user haproxy
group haproxy
daemon
defaults
log global
mode http
option httplog
option dontlognull
contimeout 5000
clitimeout 50000
srvtimeout 50000
errorfile 400 /etc/haproxy/errors/400.http
errorfile 403 /etc/haproxy/errors/403.http
errorfile 408 /etc/haproxy/errors/408.http
errorfile 500 /etc/haproxy/errors/500.http
errorfile 502 /etc/haproxy/errors/502.http
errorfile 503 /etc/haproxy/errors/503.http
errorfile 504 /etc/haproxy/errors/504.http
frontend http-frontend
bind 172.17.0.101:80
# Add "X-Forwarded-For" header with the original client's IP address
reqadd X-Forwarded-Proto:\ http
default_backend http-backend
backend http-backend
server node2 172.17.0.102:80 check
server node3 172.17.0.103:80 check- Start haproxy and enable starting on boot
Start haproxy service
root@node1:~# /etc/init.d/haproxy start
* Starting haproxy haproxyEnable haproxy start on boot
root@node1:~# update-rc.d haproxy defaults
Adding system startup for /etc/init.d/haproxy ...
/etc/rc0.d/K20haproxy -> ../init.d/haproxy
/etc/rc1.d/K20haproxy -> ../init.d/haproxy
/etc/rc6.d/K20haproxy -> ../init.d/haproxy
/etc/rc2.d/S20haproxy -> ../init.d/haproxy
/etc/rc3.d/S20haproxy -> ../init.d/haproxy
/etc/rc4.d/S20haproxy -> ../init.d/haproxy
/etc/rc5.d/S20haproxy -> ../init.d/haproxy- Log haproxy location
The default location of haproxy.log is /var/log/haproxy.log
root@node1:~# cat /var/log/haproxy.log
May 4 21:04:33 node1 haproxy[2270]: Proxy http-frontend started.
May 4 21:04:33 node1 haproxy[2270]: Proxy http-frontend started.
May 4 21:04:33 node1 haproxy[2270]: Proxy http-backend started.- Test haproxy configuration
You can use curl or access to the url http://172.17.0.101/ using a browser
root@node1:~# curl http://172.17.0.101/- Enable HAproxy stats HAproxy provides a simple web interface useful to show the status and statistics about the frontend/backend configured in haproxy and their connections.
To enable it add the following content in /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg and reload the service :
listen stats 172.17.0.101:1936
mode http
log global
maxconn 10
clitimeout 100s
srvtimeout 100s
contimeout 100s
timeout queue 100s
stats enable
stats hide-version
stats refresh 30s
stats show-node
stats auth admin:password # Change username and password for statistics webpage authentication
stats uri /haproxy?stats
Reload haproxy configuration
root@node1:~# /etc/init.d/haproxy reloadView haproxy statistics using the url http://172.17.0.101:1936/haproxy?stats
- Configure other frontend/backend with different balancing algorithms
An instance of haproxy can be configured to balance multiple services configuring multiple frontend and backend sections in its configuration file.
HAproxy allows also to define different balancing algorithms, it use round robin as default but it support other algorithms that can be selected using the option balance in backend section:
- source: This method selects which server to use based on a hash of the source IP i.e. your user’s IP address. This is one method to ensure that a user will connect to the same server
- leastconn: This method selects the server with the least number of connections. It’s recommended for longer sessions. Servers in the same backend are also rotated in a round-robin fashion.
The following configuration can be added to haproxy configuration file in order to add two other balanced service listening respectively on port 81 and 82 using leastconn and source balancing method:
frontend http-frontend1
bind 172.17.0.101:81
reqadd X-Forwarded-Proto:\ http
default_backend http-backend1
backend http-backend1
balance leastconn
server node2 172.17.0.102:80 check
server node3 172.17.0.103:80 check
frontend http-frontend2
bind 172.17.0.101:82
reqadd X-Forwarded-Proto:\ http
default_backend http-backend2
backend http-backend2
balance source
server node2 172.17.0.102:80 check
server node3 172.17.0.103:80 check