Distributed SQL Query using SparkSQL, HDFS and Sqoop
Spark SQL: A brief introduction
Spark SQL is a component of Spark framework. It allows to manipulate big unstructured data file and extract useful information using SQL. It introduces a new data abstraction called DataFrames allowing the analysis of structured and semi-structured data. Spark SQL provides API in Scala,Python and Java in order to manipulate DataFrames. It also provides the support for SQL language, a command line interface and an ODBC/JDBC server. The example described in this post shows how to write a simple Spark application in order to execute an SQL query using Spark.
Import MySQL data into HDFS
In this paragraph I show how import a MySQL database in hadoop using sqoop in the following paragraph I use this data loaded in HDFS in order to execute an SQL query.
I’m using the “world” database that can be downloaded from this [link] (https://dev.mysql.com/doc/index-other.html). It contains data about cities and countries around the world and the languages spoken in each country.
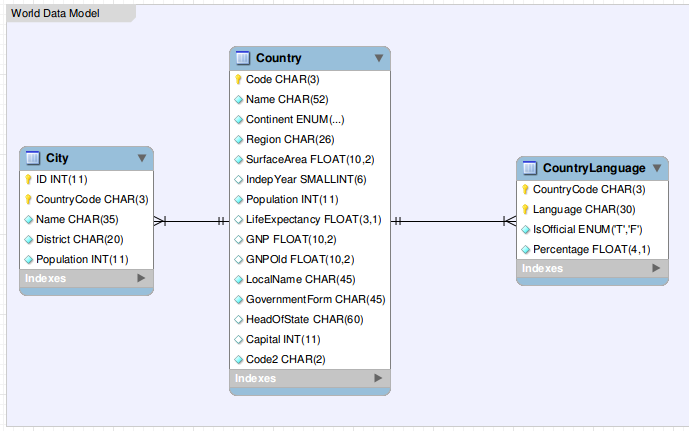
I import all tables of world database in hdfs using as output format a text file separated by tab character. The following command imports all the table in the hdfs directory /user/cloudera/world
[cloudera@quickstart ~]$ sqoop import-all-tables --connect jdbc:mysql://localhost/world --username root -P --warehouse-dir /user/cloudera/world --fields-terminated-by '\t'As you can observe watching the following command Sqoop has created a sub directory for each MySQL table and it has divided table data in different files with the same prefix “part-m-“.
[cloudera@quickstart ~]$ hadoop fs -ls /user/cloudera/world
Found 3 items
drwxr-xr-x - cloudera cloudera 0 2016-02-29 21:54 /user/cloudera/world/City
drwxr-xr-x - cloudera cloudera 0 2016-02-29 21:55 /user/cloudera/world/Country
drwxr-xr-x - cloudera cloudera 0 2016-02-29 21:55 /user/cloudera/world/CountryLanguage
[cloudera@quickstart ~]$ hadoop fs -ls /user/cloudera/world/City
Found 5 items
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 0 2016-02-29 21:54 /user/cloudera/world/City/_SUCCESS
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 37088 2016-02-29 21:54 /user/cloudera/world/City/part-m-00000
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 35361 2016-02-29 21:54 /user/cloudera/world/City/part-m-00001
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 35884 2016-02-29 21:54 /user/cloudera/world/City/part-m-00002
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 36148 2016-02-29 21:54 /user/cloudera/world/City/part-m-00003
[cloudera@quickstart ~]$ hadoop fs -cat /user/cloudera/world/City/part-m-00000|head
1 Kabul AFG Kabol 1780000
2 Qandahar AFG Qandahar 237500
3 Herat AFG Herat 186800
4 Mazar-e-Sharif AFG Balkh 127800
5 Amsterdam NLD Noord-Holland 731200
6 Rotterdam NLD Zuid-Holland 593321
7 Haag NLD Zuid-Holland 440900
8 Utrecht NLD Utrecht 234323
9 Eindhoven NLD Noord-Brabant 201843
10 Tilburg NLD Noord-Brabant 193238Spark SQL application
This paragraph describes the simple application that I wrote in order to execute the SQL Query using Spark SQL on the HDFS data imported in the last paragraph of this post.
The SQL query performs a join between all the three table of the database and it allows to extract the top ten country names and their capitals ordered by life expectancy where more than 50% of people speaks English.
First of all, i created the function “loadCSV” in order to load the data from HDFS in my application. This function accepts three parameters: the HDFS location, the name of the table used in Spark SQL and a lamba function mapping each field of HDFS text files in a specific type (string,integer,float) of a table. It parse each line of the text file in the HDFS location, split them by line and parse each line in order to extract the content of each field; at the end this function register the data on a Spark temporary table.
Later I execute the query described above and save the result on a parquet file.
from pyspark import SparkContext
from pyspark.sql import SQLContext, Row
sc = SparkContext("local", "Simple SparqSQL Join")
sqlContext = SQLContext(sc)
def loadCSV(path,tableName,function):
csv = sc.textFile(path)
columns = csv.map(lambda l: l.split("\t"))
table = columns.map(function)
schema=sqlContext.createDataFrame(table)
schema.registerTempTable(tableName)
loadCSV("/user/giovanni/world/City/*","City",
lambda p:
Row(
id=int(p[0]),
name=p[1],
countrycode=p[2],
district=p[3],
population= int(p[4])
)
)
loadCSV("/user/giovanni/world/CountryLanguage/*","CountryLanguage",
lambda p:
Row(countrycode=p[0],
language=p[1],
isofficial=p[2],
percentage=float(p[3])
)
)
loadCSV("/user/giovanni/world/Country/*","Country",
lambda p:
Row(code=p[0],
name=p[1],
continent=p[2],
region=p[3],
surfacearea=None if p[4]=='null' else float(p[4]),
indepyear=None if p[5]=='null' else int(p[5]),
population=int(p[6]),
lifeexpectancy=None if p[7]=='null' else float(p[7]),
gnp=float(p[8]),
gnpold=None if p[9]=='null' else float(p[9]),
localname=p[10],
governmentform=p[11],
headofstate=p[12],
capital=None if p[13]=='null' else int(p[13]),
code2=p[14]
)
)
outputResult = sqlContext.sql(
"""SELECT Country.name as CountryName,
Country.lifeexpectancy as CountryLifeExpectancy,
City.name as CapitalName,
CountryLanguage.language
FROM
Country JOIN City on Country.capital = City.id
JOIN
CountryLanguage ON CountryLanguage.countrycode = Country.code
WHERE CountryLanguage.language ="English"
AND CountryLanguage.percentage > 50
ORDER BY CountryLifeExpectancy desc limit 10""")
outputResult.save("sparkSQLResult")Execute the application and view the result
To run the application in my Hadoop cluster I simply wrote the source code described in the previous paragraph in the file spark_sql.py and I run it using the command spark-submit
[cloudera@quickstart ~]$ spark-submit /home/cloudera/workspace/pyspark_examples/spark_sql.pyThe next snippet use parquet tools in order to view in a human readable format the result stored in the parquet file.
[cloudera@quickstart ~]$ hadoop fs -ls /user/cloudera/sparkSQLResult
Found 4 items
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 0 2016-02-29 22:07 /user/cloudera/sparkSQLResult/_SUCCESS
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 496 2016-02-29 22:07 /user/cloudera/sparkSQLResult/_common_metadata
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 866 2016-02-29 22:07 /user/cloudera/sparkSQLResult/_metadata
-rw-r--r-- 1 cloudera cloudera 1371 2016-02-29 22:07 /user/cloudera/sparkSQLResult/part-r-00001.parquet
[root@quickstart ~]# hadoop parquet.tools.Main cat /user/cloudera/sparkSQLResult
CountryName = Australia
CountryLifeExpectancy = 79.8
CapitalName = Canberra
language = English
CountryName = Canada
CountryLifeExpectancy = 79.4
CapitalName = Ottawa
language = English
CountryName = Gibraltar
CountryLifeExpectancy = 79.0
CapitalName = Gibraltar
language = English
CountryName = Virgin Islands, U.S.
CountryLifeExpectancy = 78.1
CapitalName = Charlotte Amalie
language = English
CountryName = New Zealand
CountryLifeExpectancy = 77.8
CapitalName = Wellington
language = English
CountryName = United Kingdom
CountryLifeExpectancy = 77.7
CapitalName = London
language = English
CountryName = United States
CountryLifeExpectancy = 77.1
CapitalName = Washington
language = English
CountryName = Bermuda
CountryLifeExpectancy = 76.9
CapitalName = Hamilton
language = English
CountryName = Ireland
CountryLifeExpectancy = 76.8
CapitalName = Dublin
language = English
CountryName = Belize
CountryLifeExpectancy = 70.9
CapitalName = Belmopan
language = English