Import Mysql data in Elasticsearch server
Elasticsearch is a near real-time search server based on Lucene. It allows to create a distributed full-text search engine. It’s an opensource software developed in Java. It offers REST api in order to insert, retrieve and search data.
In this post I describe how import data from a mysql database in an elasticsearch search engine using the library https://github.com/jprante/elasticsearch-jdbc
I have already installed a Mysql server and an Elasticsearch server, you can find several documentation on internet about installation of these software.
I use the mysql example database “World” provided by mysql. It can be downloaded from the following url http://downloads.mysql.com/docs/world.sql.gz.
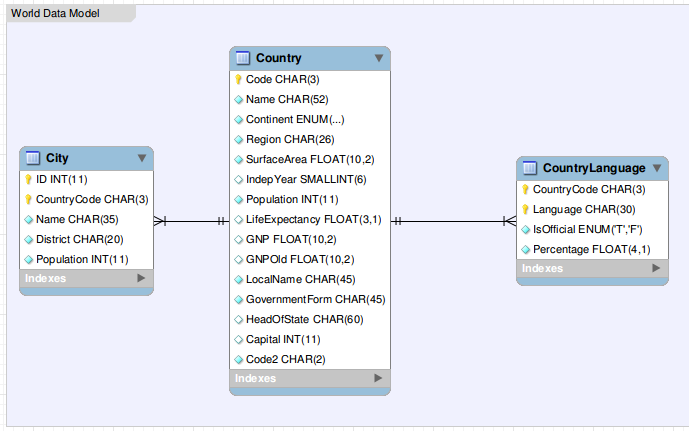
This image show the entity relationship model of this database.
Step 1
The following text box shows the command used to import the example database in mysql
root@ubuntu01:~/database_example# wget http://downloads.mysql.com/docs/world.sql.gz
root@ubuntu01:~/database_example# unzip world.sql.zip
Archive: world.sql.zip
inflating: world.sql
root@ubuntu01:~/database_example# ls
world.sql world.sql.zip
root@ubuntu01:~/database_example# mysql -uroot -p '<insert here the password>' world.sqlStep 2
Download the elasticsearch-jdbc library and create the script “mysql-import-world.sh” showed in the following text box and run it in order to import the data from Mysql to Elasticsearch.
The script contains several parameter:
- Mysql database connection data (ip, port, database name, username, passowrd)
- SQL query executed in order to extract the data. In my example I use this query:
SELECT City.ID as _id,
City.Name,
City.District,
City.Population,
Country.Name as CountryName,
Country.continent as CountryContinent
FROM City JOIN Country
ON City.CountryCode = Country.Code;- Elastic search connection data (ip, port)
- The name of the index created on Elasticsearch
root@ubuntu01:~# wget http://xbib.org/repository/org/xbib/elasticsearch/importer/elasticsearch-jdbc/2.1.0.0/elasticsearch-jdbc-2.1.0.0-dist.zip
root@ubuntu01:~# unzip elasticsearch-jdbc-2.1.0.0-dist.zip
root@ubuntu01:~# cd elasticsearch-jdbc-2.1.0.0/bin/
root@ubuntu01:~/elasticsearch-jdbc-2.1.0.0/bin# cat ./mysql-import-world.sh
#!/bin/bash
DIR="$( cd "$( dirname "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" ; pwd )"
bin=${DIR}/../bin
lib=${DIR}/../lib
echo '
{
"type" : "jdbc",
"jdbc" : {
"url" : "jdbc:mysql://172.17.0.101:3306/world",
"user" : "root",
"password" : "password",
"sql" : "select City.ID as _id,City.Name,City.District,City.Population,Country.Name as CountryName, Country.continent as CountryContinent from City JOIN Country ON City.CountryCode = Country.Code;",
"treat_binary_as_string" : true,
"elasticsearch" : {
"cluster" : "elasticsearch",
"host" : "172.17.0.101",
"port" : 9300
},
"max_bulk_actions" : 20000,
"max_concurrent_bulk_requests" : 10,
"index" : "world"
}
}
' | java \
-cp "${lib}/*" \
-Dlog4j.configurationFile=${bin}/log4j2.xml \
org.xbib.tools.Runner \
org.xbib.tools.JDBCImporter
root@ubuntu01:~/elasticsearch-jdbc-2.1.0.0/bin# ./mysql-import-world.shStep 3
Finally execute a query to the Elasticsearch server in order to verify that the new index world has been created and a second query in order to retrieve some articles from this index.
[root@ubuntu01:~/elasticsearch-jdbc-2.1.0.0/bin] # curl 'http://localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v'
health status index pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
green open world 5 1 4079 0 1.1mb 1.1mb
green open settings 5 1 0 0 650b 650b
[root@ubuntu01:~/elasticsearch-jdbc-2.1.0.0/bin] # curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/world/_search?size=3&amp;amp;pretty=true'
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 4079,
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [ {
"_index" : "world",
"_type" : "jdbc",
"_id" : "129",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source":{"Name":"Oranjestad","District":"Aruba","Population":29034,"CountryName":"Aruba","CountryContinent":"North America"}
}, {
"_index" : "world",
"_type" : "jdbc",
"_id" : "60",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source":{"Name":"Namibe","District":"Namibe","Population":118200,"CountryName":"Angola","CountryContinent":"Africa"}
}, {
"_index" : "world",
"_type" : "jdbc",
"_id" : "73",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source":{"Name":"Lomas de Zamora","District":"Buenos Aires","Population":622013,"CountryName":"Argentina","CountryContinent":"South America"}
} ]
}
}There are also some software like Kibana and Graphana providing a dashboard really useful to query an elasticsearch server and show the data in a web interface.