Flume: Import apache logs in hadoop hdfs
Flume is a project of the Apache Software Foundation used to import stream of data to a centralized data store. In hadoop environments Flume is used to import data into hadoop clusters from different data sources.
In this post I show how use Flume to import apache logs (access_log and error_log ) in hadoop hdfs filesystem.
A Flume agent is composed by a set of sources, channel and sinks:
- sources are used to collect data/events from different data sources
- channels are the communication media used to temporary store the events collected by the sources
- sinks asynchronously read the events from the channel and send them to a destination
Flume supports different types of sources,channels and sinks. The complete list of sources,channel and sinks already implemented can be obtained reading the documentation ( https://flume.apache.org/FlumeUserGuide.html )
In my example in order to import Apache web server logs I use the following flume component:
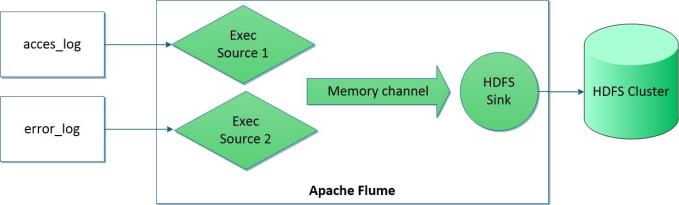
- Exec source: It runs a unix command and expects that process produce data in the standard output
- Memory channel: This channel implements an in-memory queue for the events
- HDFS Sync: It allows to create text file on HDFS The following image shows the architecture of the flume agent used in this example.
The flume agent requires a configuration file defining the sources,channels and sinks used by the agent and their properties. The following text box shows the flume configuration file that I used to import apache web server logs in hadoop:
##### /home/cloudera/example-1.conf
# Name the components on this agent
# I define two sources:
# a source for access log file
# a source for for error log file
agent1.sources = tailAccessSource tailErrorSource
# I define one sink
agent1.sinks = hdfsSink
# I define one channel
agent1.channels = memChannel01
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
# Both sources will use the memory channel
agent1.sources.tailAccessSource.channels = memChannel01
agent1.sources.tailErrorSource.channels = memChannel01
agent1.sinks.hdfsSink.channel = memChannel01
# Define the type and options for each sources
agent1.sources.tailAccessSource.type = exec
agent1.sources.tailAccessSource.command = tail -F /var/log/httpd/access_log
agent1.sources.tailErrorSource.type = exec
agent1.sources.tailErrorSource.command = tail -F /var/log/httpd/error_log
# Define the type and options for the channel
agent1.channels.memChannel01.type = memory
agent1.channels.memChannel01.capacity = 100000
agent1.channels.memChannel01.transactionCapacity = 10000
# Define the type and options for the sink
# Note: namenode is the hostname the hadoop namenode server
# flume/data-example.1/ is the directory where the apache logs will be stored
agent1.sinks.hdfsSink.type = hdfs
agent1.sinks.hdfsSink.hdfs.path = hdfs://namenode/flume/data-example.1/
agent1.sinks.hdfsSink.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
agent1.sinks.hdfsSink.hdfs.rollCount = 0
agent1.sinks.hdfsSink.hdfs.rollSize = 0
agent1.sinks.hdfsSink.hdfs.rollInterval = 60The import of apache logs can be started running Flume with its configuration file as argument and waiting that Apache web server start to produce logs:
[cloudera@quickstart ~]$ flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file /home/cloudera/example-1.conf --name agent1 -Dflume.root.logger=DEBUG,console